pseudomembranous colitis in babies
It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Antibiotic-associated colitis is a rare complication of antimicrobial therapy in children.
Clostridioides Difficile Infection Wikiwand
It is most often seen in people who are in the hospital.
. Frequent watery diarrhea that is sometimes bloody. Difficile infection is uncommon in children. The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years.
This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children. Wall thickening was confined to the left colon and rectum in 29 22 to the right colon in 29 22 and involved the whole colon in 39 33. Jayakar AV Desai AG Dalal NJ Shah SC Narayan K.
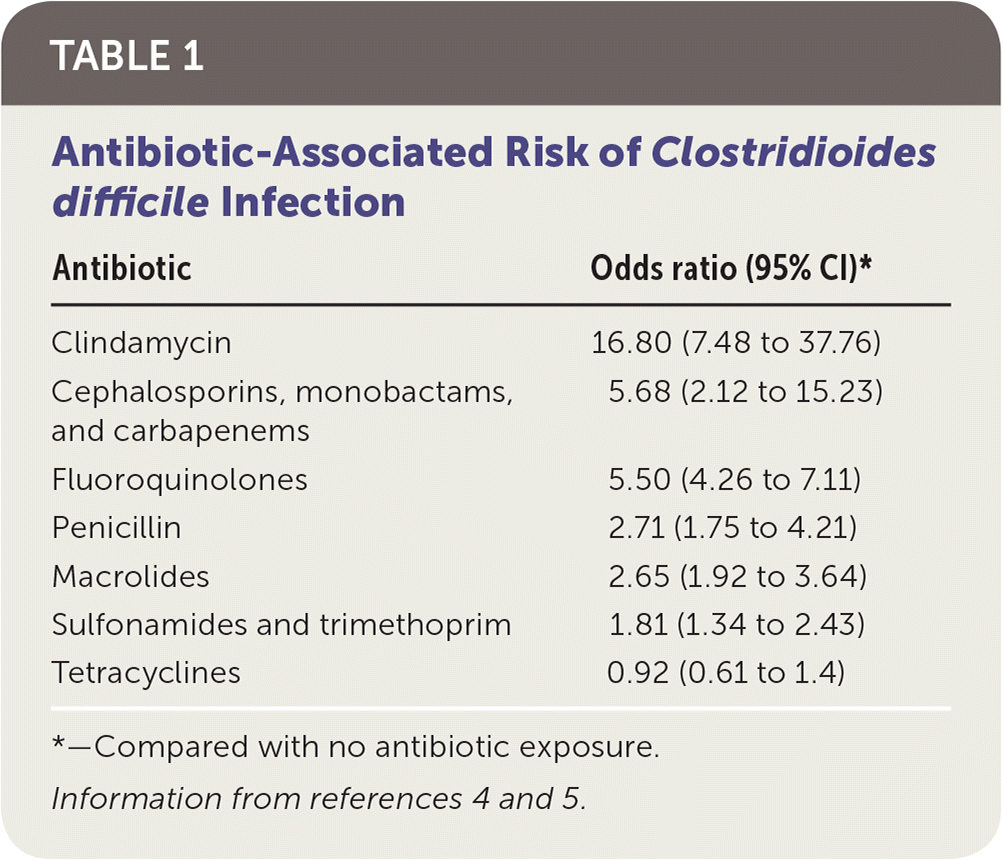
Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a cytopathic toxin which was neutralized by Clostridium sordellii. Ampicillin penicillin and clindamycin are the drugs most frequently reported to cause pseudomembranous colitis in pediatric patients. The clinical spectrum of this disease may range from a mild non-specific.
There are limited descriptions of pseudomembranous colitis in children. This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children. The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years.
For most children who have symptoms they are quite mild and include. Pseudomembranous colitis is uncommon in children and rare in infants. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs mainly in adults and is believed to be caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile.
Other findings included pericolonic edema in 39 33 and ascites in 19 11. Up to 10 cash back A spectrum of nodular haustral thickening and an accordion pattern have been reported as specific features of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in adults. Toxic megacolon can occur as a complication of.
Symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis include. 3 A child with this condition may experience many or all of the following symptoms. Diff can cause a type of inflammation of the colon large intestine called pseudomembranous colitis.
However it is becoming more common in people who take antibiotics and are not in a hospital. Pseudomembranous colitis after short-course antibiotics is rare in children. PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization.
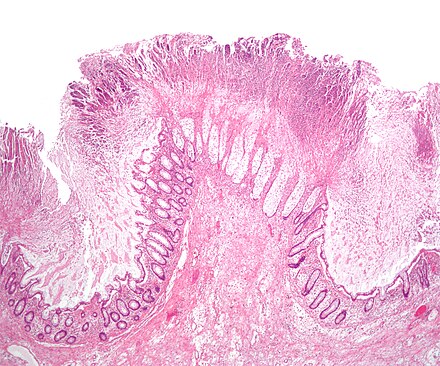
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. Pseudomembranous colitis is an inflammatory condition of the colon characterized by elevated yellow-white plaques that coalesce to form pseudomembranes on the mucosa. Bolton RP Thomas DF.
This diagnosis should be suspected in any child with significant diarrhea during or after a course of antimicrobial. The clinical spectrum of this disease may range from a mild non-specific diarrhea to severe colitis. 1 Childrens Hospital of Shanxi Elimination of the Division Taiyuan Shanxi.
Pseudomembranous colitis severe inflammation of the inner lining of the bowel from C. It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Approach to diarrhea in children in resource-rich countriessystemic toxicity.
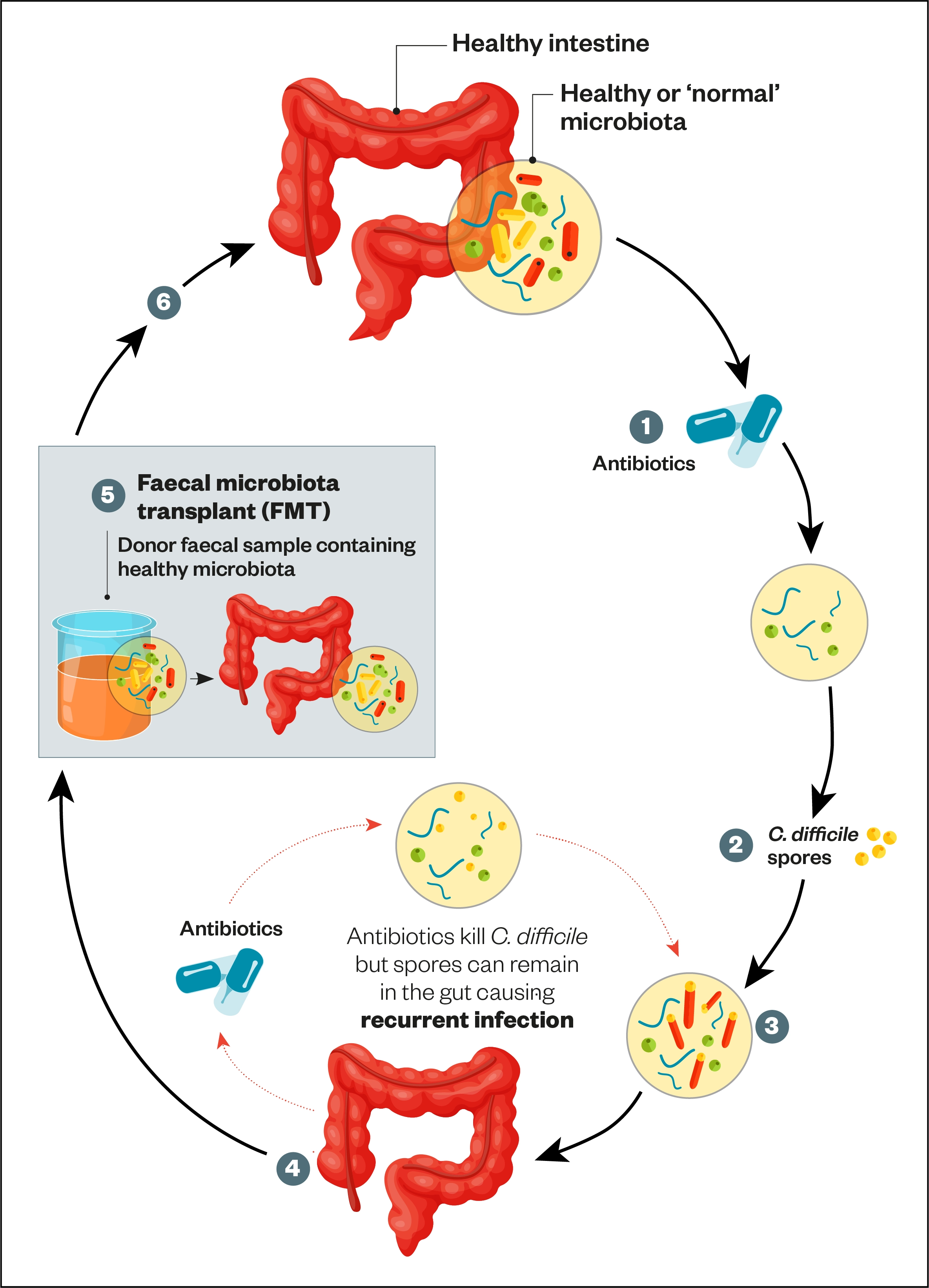
Identification of Clostridium difficile as the major pathogen has led to a rational successful approach to therapy and has widened the spectrum of associated disease. PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization. Use of medicines that weaken the immune system such as chemotherapy medicines.
In four girls and five boys CT scans were. Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a c. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed.
In more severe cases sepsis the bodys potentially dangerous overreaction to an infection can occur. Pseudomembranous colitis in children and adults. The clinical spectrum of this disease may range from a mild non-specific.
PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization. Its rare for young children or infants to get PMC. It is commonly isolated from stool samples of children but has been associated with infections in different systems and bacteremia.
The clinical spectrum of this disease may range from a mild non-specific. 127 There are reports of C. It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile.
PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization. Pseudomembranous colitis remains a potentially lethal complication of antibiotic usage. Although CT findings associated with PMC in children may be suggestive for this diagnosis CT is less specific.
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC is inflammation in your colon that happens when theres too much of certain bacteria in your system. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed.
It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children. We report a 14-month-old girl who presented with rectal prolapse complicated with.
Colonoscopy found that PMC occurs mainly in the colon sigmoid colon and rectum in up to 80 100 of cases. Pseudomembranous colitis in children. This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children.
A retrospective review of nine patients with PMC was performed to assess whether this spectrum of CT findings also occurred in children. Pain and tenderness in the stomach.

Clostridium Difficile Infection What You Need To Know Consultant360
Colitis Types Diagnosis And Treatment

Lactobacillus Reuteri Dsm 17938 In The Prevention Of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea In Children A Randomized Clinical Trial Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Infections Caused By C Difficile In Children Explained Wonderbaba

Pin On Learn Pediatrics Child Health Through Mcqs Toacs

Clostridium Difficile C Diff Infectious Dis Medbullets Step 2 3

Clostridium Difficile C Diff Infectious Dis Medbullets Step 2 3

A Diverticular Colitis Endoscopic Picture B Histological Aspect Download Scientific Diagram

Pediatrics Mcqs Toacs Pearls Updates Cardiovascular System Examination Approach Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular Signs Of Heart Failure
Clostridioides Difficile Infection Update On Management

Pseudomembranous Colitis Accordion Colitis
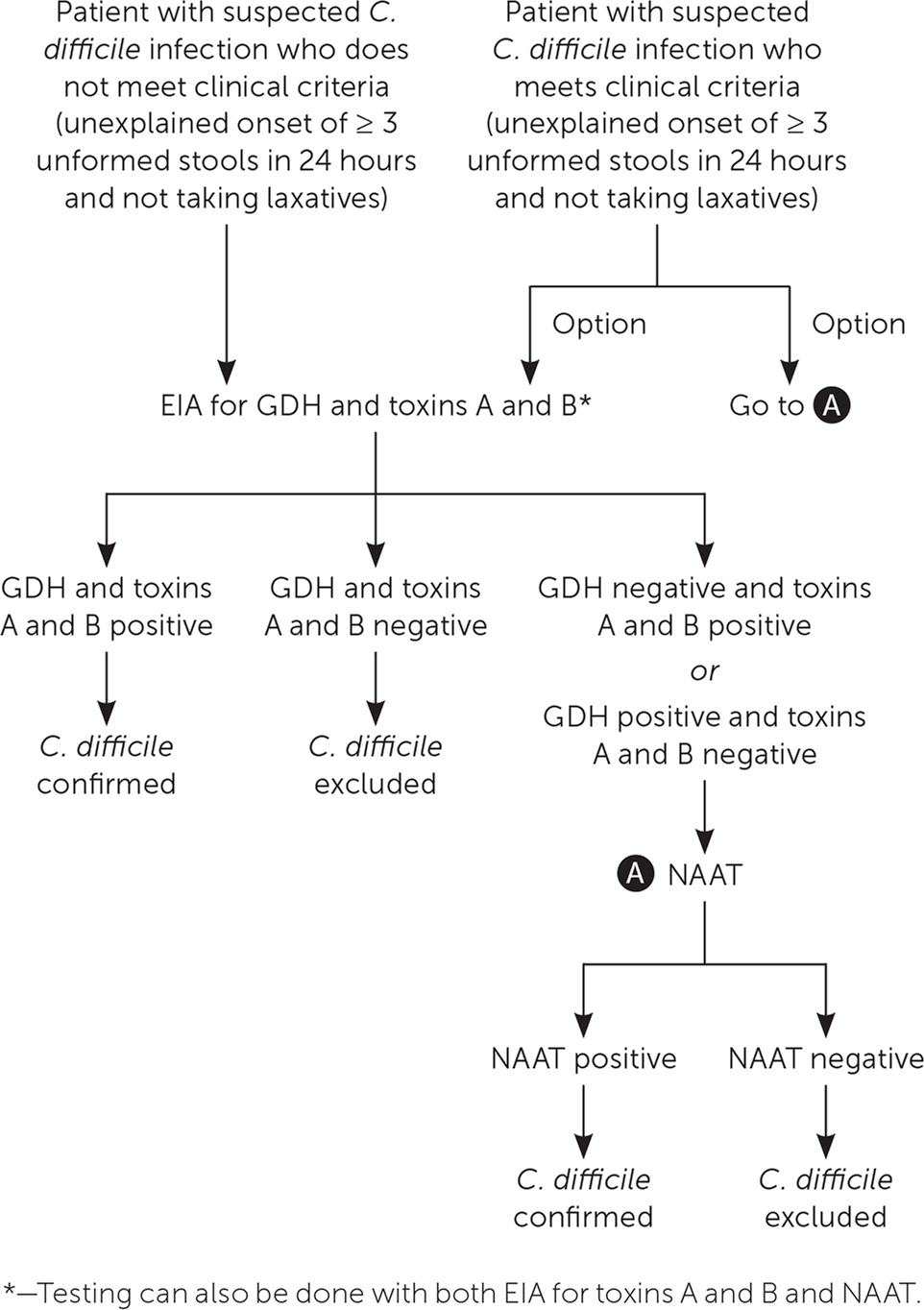
Clostridioides Difficile Infection Update On Management

What Is Enterocolitis Causes Symptoms Treatment Diet

Clostridioides Difficile Infection Management The Pharmaceutical Journal

Clostridium Difficile C Diff Infectious Dis Medbullets Step 2 3
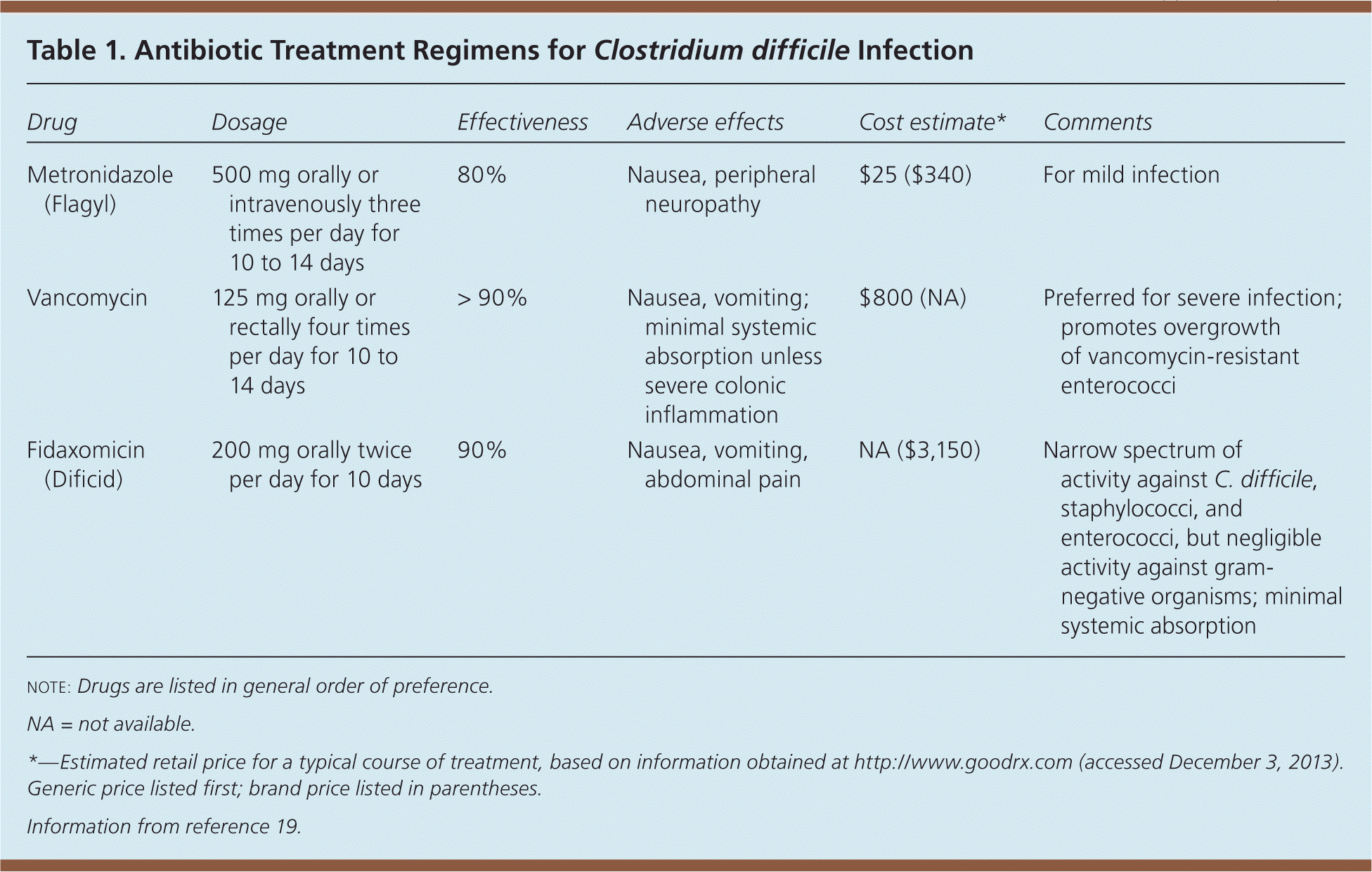
Common Questions About Clostridium Difficile Infection
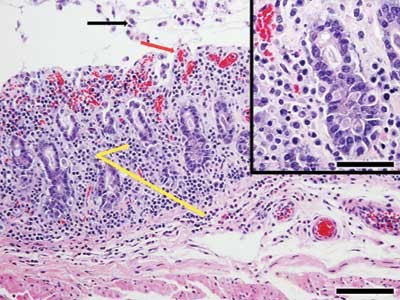
Diagnosis Clostridium Difficile Induced Typhlitis And Colitis Lab Animal
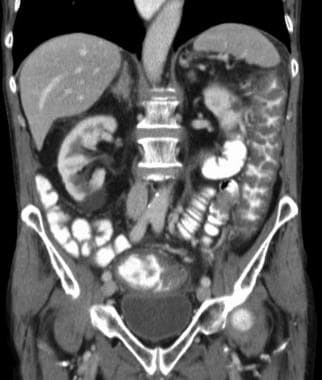
Clostridioides Clostridium Difficile Colitis Workup Approach Considerations Stool Examination And Stool Assays Endoscopy

C Diff Colitis Irritable Bowel Disease Pseudomembranous Colitis C Diff